Highlights
Kerr and Raman beam cleanup with supercontinuum generation in multimode microstructure fiber
We experimentally study the interplay of Kerr and Raman beam cleanup in multimode air-silica microstructure optical fiber. The interplay of modal four-wave mixing and Raman scattering leads to high-brightness multimode supercontinuum
R. Dupiol, K. Krupa, A. Tonello, M. Fabert, D. Modotto, S. Wabnitz, G. Millot, S. Wabnitz, and V. Couderc, “Interplay of Kerr and Raman beam cleaning with a multimode microstructure fiber”, Optics Letters 43, 587-590 (2018)
Intermodal Modulation Instability and Four-Wave Mixing in Graded-Index Few-Mode Fibers
By controlling pump modes injected in the normal dispersion regime of few-mode graded index optical fiber, we investigated intermodal noise-seeded modulation instability and generation of highly-detuned cascaded intermodal four-wave mixing sidebands
Dupiol R., Bendahmane A., Krupa K., Tonello A., Fabert M., Kibler B., Sylvestre T., Barthelemy A., Couderc V., Wabnitz S., Millot G., Far-detuned cascaded intermodal four-wave mixing in a multimode fiber. Opt. Lett., vol. 42, p. 1293-1296, (2017)
Dupiol R., Bendahmane A., Krupa K., Fatome J., Tonello A., Fabert M., Couderc V., Wabnitz S., Millot G., Intermodal modulational instability in graded-index multimode optical fibers. Opt. Lett., vol. 42, p. 3419-3422, (2017)
Abdelkrim Bendahmane, Katarzyna Krupa, Alessandro Tonello, Daniele Modotto, Thibaut Sylvestre, Vincent Couderc, Stefan Wabnitz, and Guy Millot, “Seeded intermodal four-wave mixing in a highly multimode fiber,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 35, 295-301 (2018)
Nonlinear polarization dynamics of Kerr beam self-cleaning in GRIN multimode optical fiber
We experimentally study the polarization dynamics of Kerr beam self-cleaning in a multimode fiber. We reveal that spatial beam cleanup is accompanied by nonlinear polarization evolution and a significant increase of the degree of polarization.
Katarzyna Krupa, Graciela Garmendia Castañeda, Alessandro Tonello, Alioune Niang, Denis S. Kharenko, Marc Fabert, Vincent Couderc, Guy Millot, Umberto Minoni, Daniele Modotto, Stefan Wabnitz, “Nonlinear polarization dynamics of Kerr beam self-cleaning in a GRIN multimode optical fiber”, Opt. Lett. 44, 171-174 (2019)
Spatiotemporal light beam compression from nonlinear mode coupling
Kerr beam self-cleaning in graded-index multimode fibers is accompanied by power-dependent temporal pulse reshaping. We explore the complex nonlinear dynamics with a single long pulse, where the optical power is continuously varied across its profile.
K. Krupa, A. Tonello, V. Couderc, A. Barthelemy, G. Millot, D. Modotto, and S. Wabnitz, “Spatiotemporal light beam compression from nonlinear mode coupling”, Physical Review A, vol. 97, 043836 (2018)
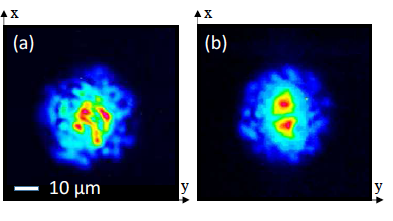
Modal attraction on low-order modes by Kerr effect in GRIN MMF
Modal attraction towards low order modes in a GRIN multimode fiber was experimentally observed at high power and characterized, thus enriching the dynamics of the Kerr self-cleaning effect leading to quasi fundamental mode generation.
E. Deliancourt, M. Fabert, A. Tonello, K. Krupa, A. Desfarges-Berthelemot, V. Kermene, G. Millot, A. Barthélémy, S. Wabnitz, and V. Couderc, “Kerr beam self-cleaning on the LP11 mode in graded-index multimode fibers,” OSA Continuum 2, 1089-1096 (2019); https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.00563n
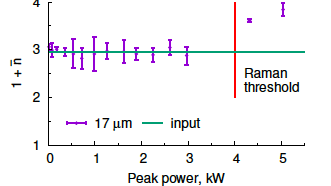
Hydrodynamic 2D turbulence and spatial beam condensation in multimode optical fibers
We experimentally demonstrate the conservation of the average mode number in the process of Kerr beam self-cleaning in a graded-index multimode optical fiber, in analogy with wave condensation in hydrodynamic 2D turbulence.
E. V. Podivilov, D. S. Kharenko, V. A. Gonta, K. Krupa, O. S. Sidelnikov, S. Turitsyn, M. P. Fedoruk, S. A. Babin, S. Wabnitz, “Hydrodynamic 2D turbulence and spatial beam condensation in multimode optical fibers”, Physical Review Letters, vol. 122, 103902 (2019); https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.10239
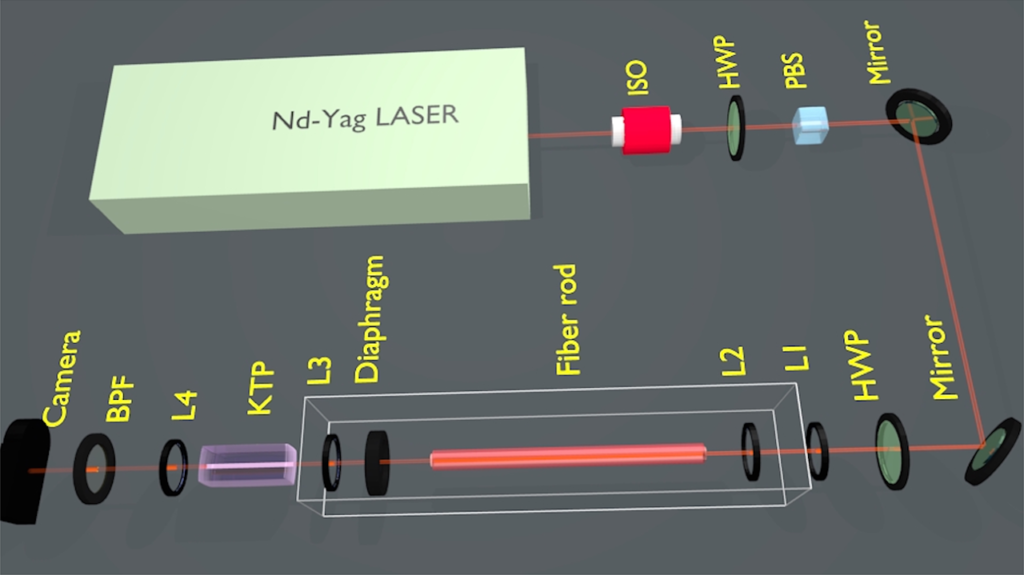
erc-stems – SHG
Spatial beam self-cleaning in second-harmonic generation
We experimentally demonstrate the spatial self-cleaning of a highly multimode optical beam, in the process of second-harmonic generation in a quadratic nonlinear potassium titanyl phosphate crystal.
Krupa, K., Fona, R., Tonello, A. et al. Spatial Beam Self-Cleaning in Second-Harmonic Generation. Sci Rep 10, 7204 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64080-7
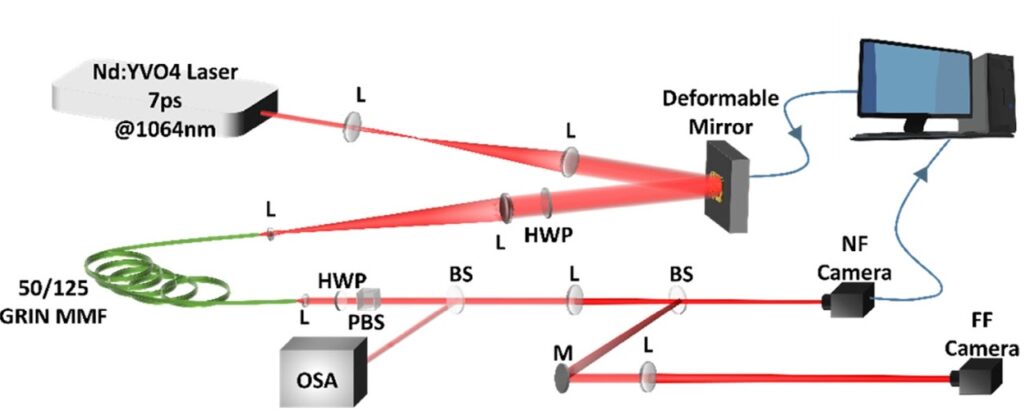
erc-stems -MANY MODES
Wavefront shaping for optimized many-mode Kerr beam self-cleaning in graded-index multimode fiber
We experimental demonstrated that the Kerr beam self-cleaning of many low-order modes in a graded-index multimode fiber can be controlled thanks to optimized wavefront shaping of the coherent excitation beam. Adaptive profiling of the transverse input phase was utilized for channeling the launched power towards a specific low-order fiber mode, by exploiting nonlinear coupling among all guided modes.
E. Deliancourt, M. Fabert, A. Tonello, K. Krupa, A. Desfarges-Berthelemot, V. Kermene, G. Millot, A. Barthélémy, S. Wabnitz, and V. Couderc, “Wavefront shaping for optimized many-mode Kerr beam self-cleaning in graded-index multimode fiber,” Opt. Express 27, 17311-17321 (2019), https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.27.017311
erc-stems- TELECOM
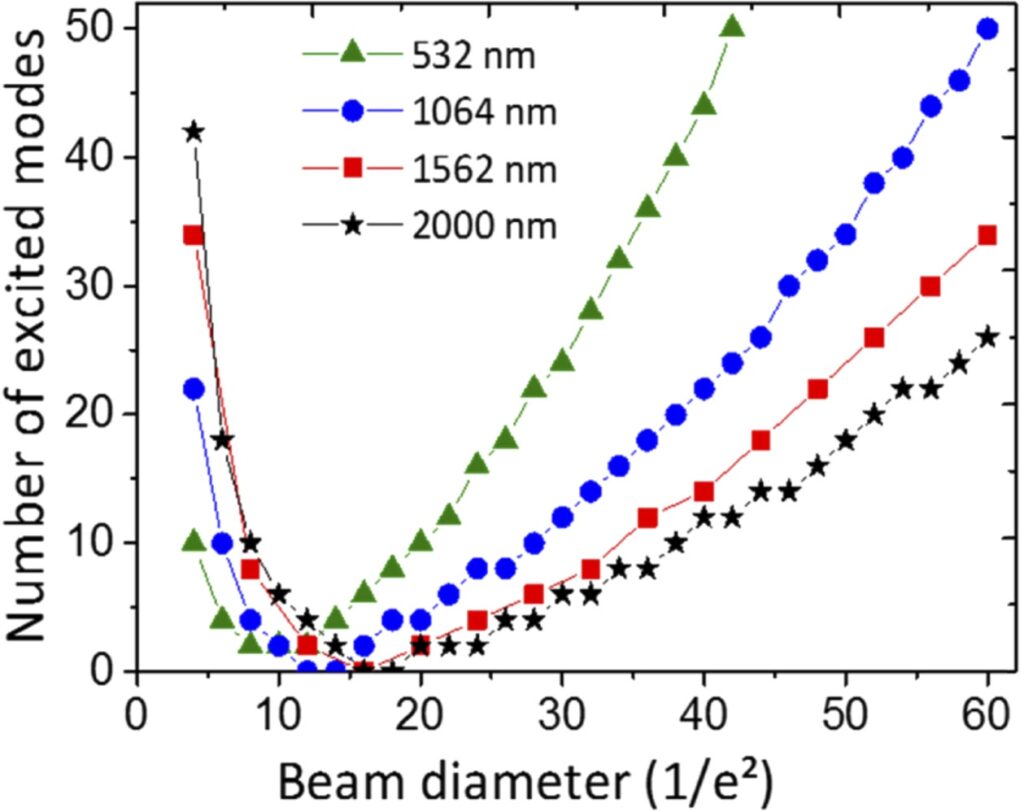
Highly efficient few-mode spatial beam self-cleaning at 1.5µm
We experimentally demonstrate that spatial beam self-cleaning can be highly efficient when obtained with a few-mode excitation in graded-index multimode optical fibers. By using 160 ps long, highly chirped (6 nm bandwidth at -3dB) optical pulses at 1562 nm, we demonstrate a one-decade reduction of the power threshold for spatial beam self-cleaning, with respect to previous experiments using pulses with laser wavelengths at 1030-1064 nm. Self-cleaned beams remain spatio-temporally stable for more than a decade of their peak power variation.
Y. Leventoux, A. Parriaux, O. Sidelnikov, G. Granger, M. Jossent, L. Lavoute, D. Gaponov, M. Fabert, A. Tonello, K. Krupa, A. Desfarges-Berthelemot, V. Kermene, G. Millot, S. Février, S. Wabnitz, and V. Couderc, “Highly efficient few-mode spatial beam self-cleaning at 1.5µm,” Opt. Express 28, 14333-14344 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.392081
erc-stems- SHAPING
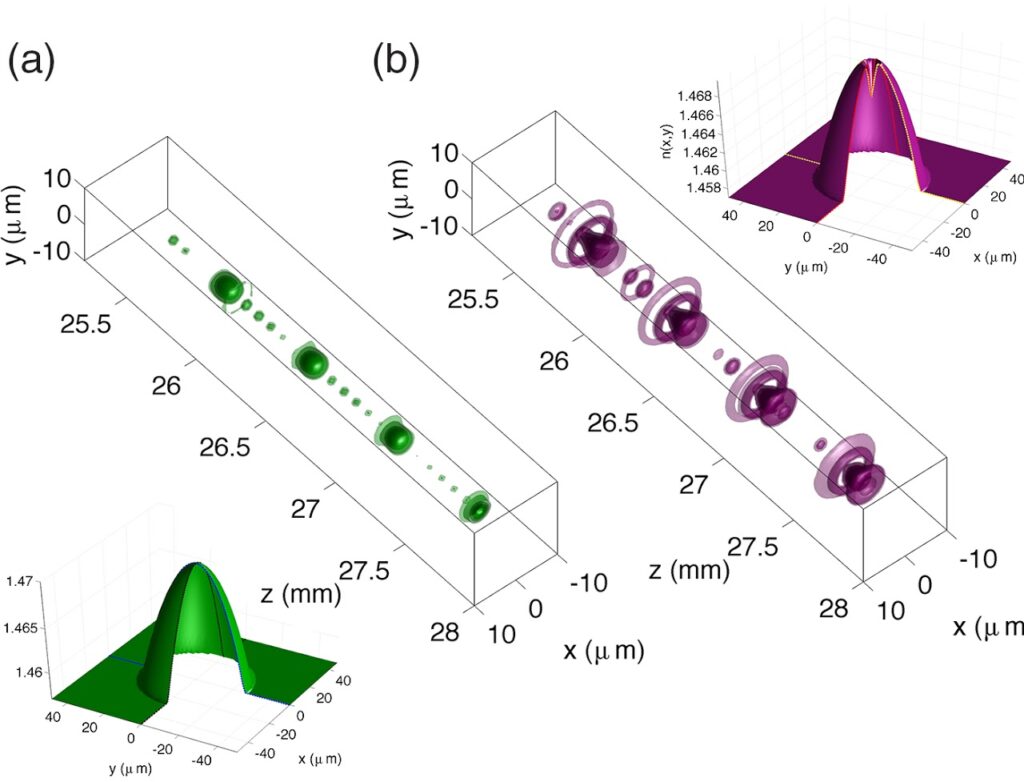
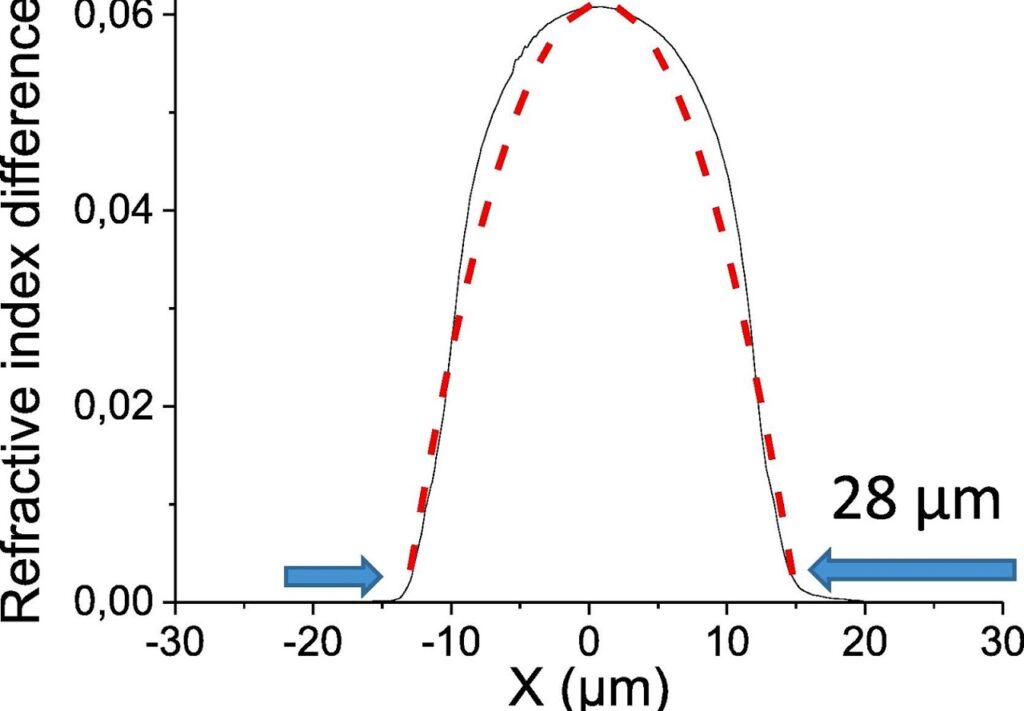
We introduce the concept of spatial and spectral control of nonlinear parametric sidebands in multimode optical fibers by tailoring their linear refractive index profile. Our experiments show that introducing a Gaussian dip into the refractive index profile of a graded index fiber permits us to dramatically change the spatial content of spectral sidebands into higher-order modes.
Katarzyna Krupa, Vincent Couderc, Alessandro Tonello, Daniele Modotto, Alain Barthélémy, Guy Millot, and Stefan Wabnitz, “Refractive index profile tailoring of multimode optical fibers for the spatial and spectral shaping of parametric sidebands,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 36, 1117-1126 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.36.001117
erc-stems-MLASC
Spatial beam self-cleaning in multimode lanthanum aluminum silicate glass fiber
We demonstrate that spatial Kerr beam self-cleaning can be obtained in a highly multimode multicomponent optical fiber based on lanthanum aluminum silicate oxide glasses (SiO2-Al2O3-La2O3), made by using the modified powder in tube technology (MIPT). We show how such fabrication method can provide interesting potentialities to design doped multimode optical fibers with homogeneous and quasi-parabolic refractive-index core profile for nonlinear optics applications.
Romain Guénard, Katarzyna Krupa, Alessandro Tonello, Marc Fabert, Jean-Louis Auguste, Georges Humbert, Stéphanie Leparmentier, Jean-René Duclère, Sébastien Chenu, Gaëlle Delaizir, Guy Millot, Daniele Modotto, Stefan Wabnitz, Vincent Couderc, Spatial beam self-cleaning in multimode lanthanum aluminum silicate glass fiber, Optical Fiber Technology, Volume 53, 2019, 102014, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2019.102014
erc-stems-RANDOM
Random mode coupling assists Kerr beam self-cleaning in a graded-index multimode optical fiber
We numerically investigate the process of beam self-cleaning in a graded-index multimode optical fiber, by using the coupled-mode model. We introduce various models of random linear coupling between spatial modes, including coupling between all modes, or only between degenerate ones, and investigate the effects of random mode coupling on the beam self-cleaning process. The results of numerical investigations are in complete agreement with our experimental data.
Oleg S. Sidelnikov, Evgeniy V. Podivilov, Mikhail P. Fedoruk, Stefan Wabnitz, Random mode coupling assists Kerr beam self-cleaning in a graded-index multimode optical fiber, Optical Fiber Technology, Volume 53, 2019, 101994 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2019.101994
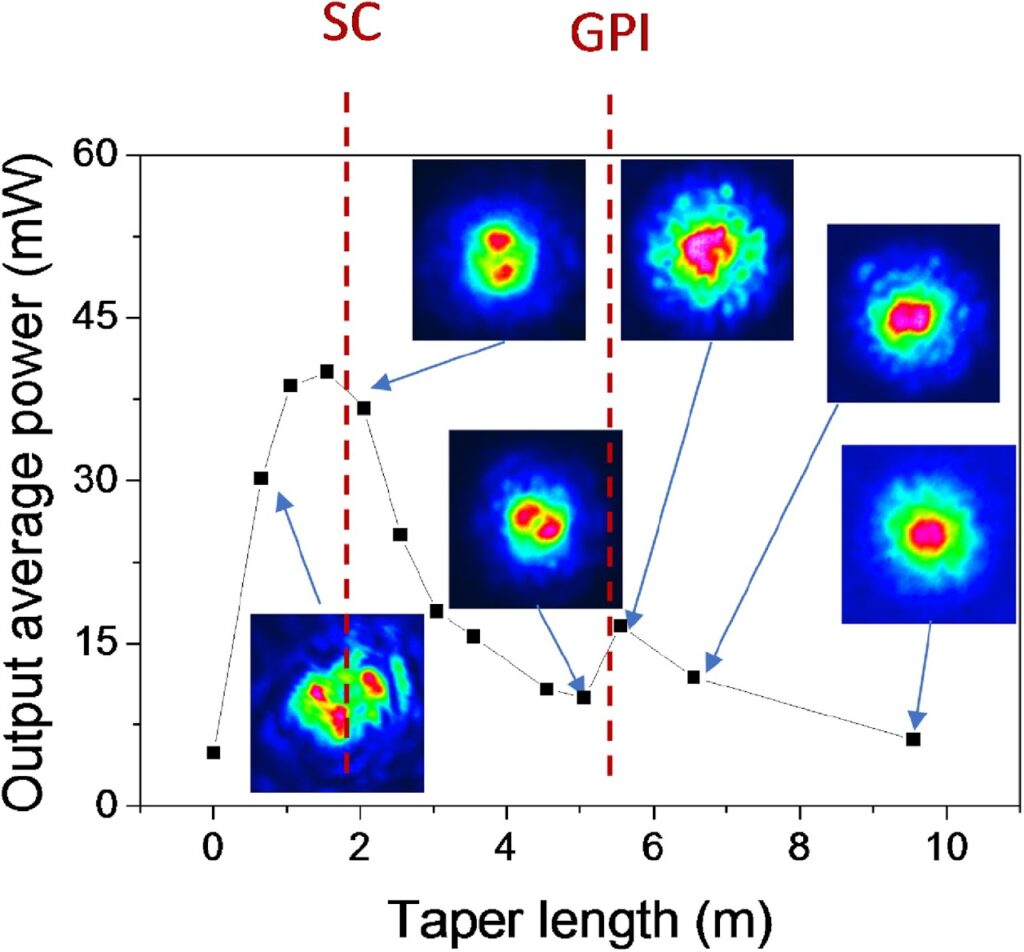
erc-stems-ACCELERATE
We experimentally demonstrate spatial beam self-cleaning and supercontinuum generation in a tapered Ytterbium-doped multimode optical fiber with parabolic core refractive index profile when 1064 nm pulsed beams propagate from the wider into the smaller diameter. In the passive mode, increasing the input beam peak power above 20 kW leads to a bell-shaped output beam profile. In the active configuration, gain from the pump laser diode permits to combine beam self-cleaning with supercontinuum generation between 520-2600 nm. By taper cut-back, we observed that the dissipative landscape, i.e., a non-monotonic variation of the average beam power along the MMF, leads to modal transitions of self-cleaned beams along the taper length.
A. Niang, T. Mansuryan, K. Krupa, A. Tonello, M. Fabert, P. Leproux, D. Modotto, O. N. Egorova, A. E. Levchenko, D. S. Lipatov, S. L. Semjonov, G. Millot, V. Couderc, and S. Wabnitz, “Spatial beam self-cleaning and supercontinuum generation with Yb-doped multimode graded-index fiber taper based on accelerating self-imaging and dissipative landscape,” Opt. Express 27, 24018-24028 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.27.024018
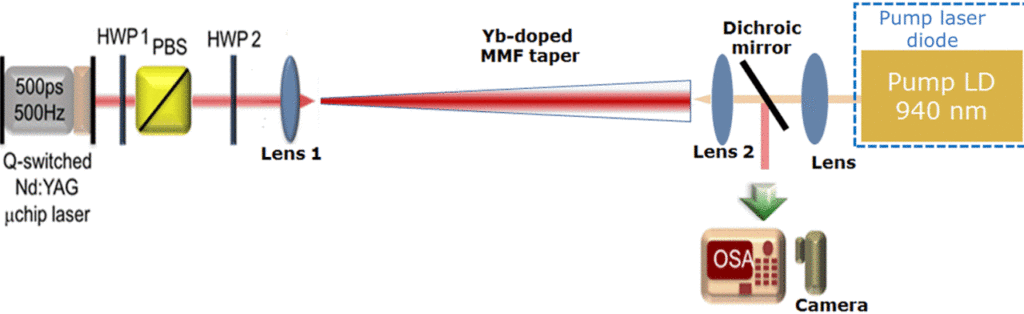
erc-stems-DECELERATE
Spatial Beam Self-Cleaning in Tapered Yb-Doped GRIN Multimode Fiber With Decelerating Nonlinearity
We experimentally demonstrate spatial beam self-cleaning in an Yb-doped graded-index multimode fiber taper, both in passive and active configurations. The input laser beam at 1064 nm was injected for propagation from the small to the large core side of the taper, with laser diode pumping in a counterdirectional configuration. The Kerr effect permits to obtain high-beam quality amplification with no accompanying frequency conversions. As a result, our nonlinear taper amplifier may provide an important building block for multimode fiber lasers and amplifiers.
A. Niang et al., “Spatial Beam Self-Cleaning in Tapered Yb-Doped GRIN Multimode Fiber With Decelerating Nonlinearity,” in IEEE Photonics Journal, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1-8, April 2020, Art no. 6500308. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2020.2979938
erc-stems-BULLETS
Finding spatiotemporal light bullets in multicore and multimode fibers
A two-level iterative algorithm for finding stationary solutions of coupled nonlinear Schrödinger equations describing the propagation dynamics of an electromagnetic pulse in multimode and multicore optical fibers of various structures was developed and tested. Using as an example the proposed analytical soliton solution which is localized in space and time, test calculations were performed, and the convergence of the algorithm was demonstrated.
I. S. Chekhovskoy, O. V. Shtyrina, S. Wabnitz, and M. P. Fedoruk, “Finding spatiotemporal light bullets in multicore and multimode fibers,” Opt. Express 28, 7817-7828 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.384464
erc-stems-SPATIOTEMPORAL
Spatiotemporal Mode-Locking in a Fiber Laser
We introduce a spatiotemporal mode-locking mechanism in a fiber (or waveguide) laser, based on nonlinear mode-cleaning enhanced by graded dissipation. Our analysis is based on the generalized dissipative Gross-Pitaevskii equation, which has a broad impact in nonlinear physics, including nonlinear optics and Bose-Einstein condensates. We demonstrate that a careful control of dissipative and non-dissipative physical mechanisms results in the self-emergence of stable (2+1)-dimensional dissipative solitons. Achieving such a regime does not require any additional mode-locking mechanisms, and allows for stable energy (or”mass”) harvesting by coherent localized structures, such as ultrashort laser pulses or Bose-Einstein condensates.
V. Kalashnikov and S. Wabnitz, Spatiotemporal Mode-Locking in a Fiber Laser (2020) https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.00990
erc-stems-SOLITONS
High-energy soliton fission dynamics in multimode GRIN fiber
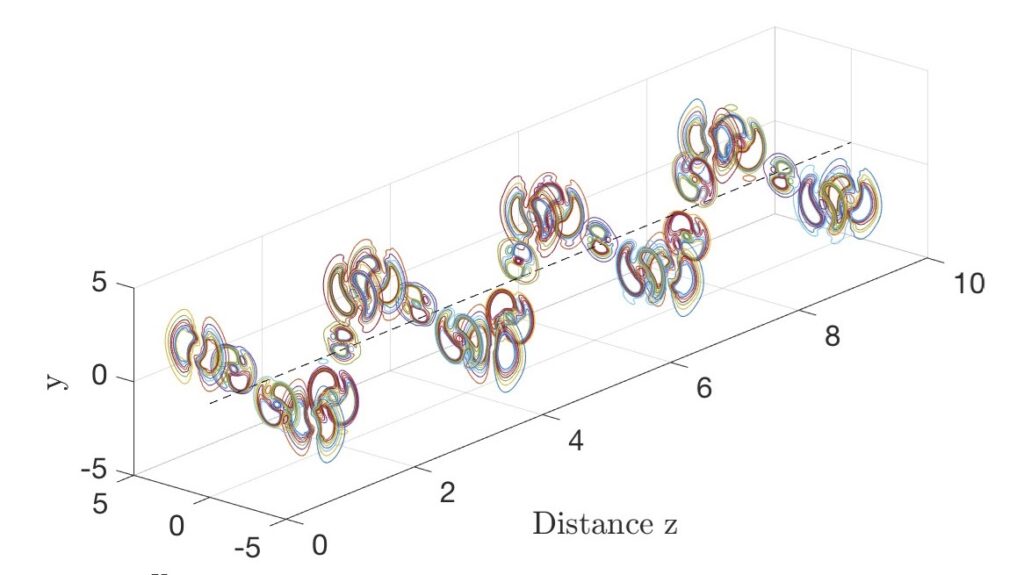
The process of high-energy soliton fission is experimentally and numerically investigated in a graded-index multimode fiber. Fission dynamics is analyzed by comparing numerical observations and simulations. A novel regime is observed, where solitons produced by the fission have a nearly constant Raman wavelength shift and same pulse width over a wide range of soliton energies
Mario Zitelli, Fabio Mangini, Mario Ferraro, Alioune Niang, Denis Kharenko, Stefan Wabnitz, High-energy soliton fission dynamics in multimode GRIN fiber (2020) https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.008
erc-stems-SELF-IMAGING
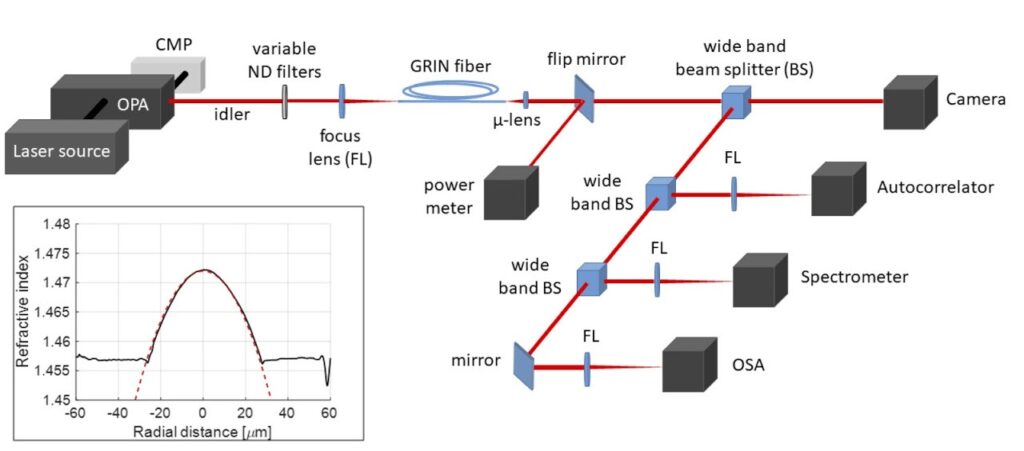
Beam-self imaging in nonlinear graded-index multimode optical fibers is of interest for many applications, such as implementing a fast saturable absorber mechanism in fiber lasers via multimode interference. We obtain an exact solution for the nonlinear evolution of first and second order moments of a laser beam carried by a graded-index multimode fiber, predicting that the spatial self-imaging period does not vary with power. Whereas the amplitude of the oscillation of the beam width is power-dependent. We experimentally studied the longitudinal evolution of beam self-imaging by means of femtosecond laser pulse propagation in both the anomalous and the normal dispersion regime of a standard telecom graded-index multimode optical fiber. Light scattering out of the fiber core via visible fluorescence emission and harmonic wave generation permits us to directly confirm that the self-imaging period is invariant with power. Spatial shift and splitting of the self-imaging process under the action of self-focusing is also observed.
erc-stems-PERSPECTIVE
Multimode nonlinear fiber optics, a spatiotemporal avenue
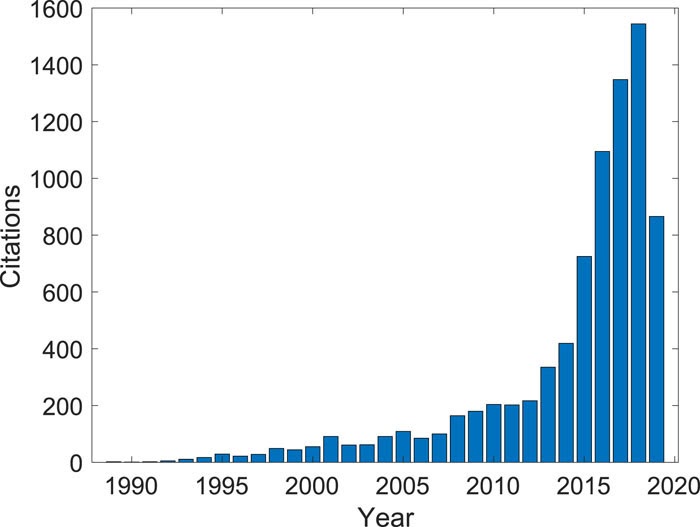
We provide a perspective overview of the emerging field of nonlinear optics in multimode optical fibers. These fibers enable new methods for the ultrafast light-activated control of temporal, spatial, and spectral degrees of freedom of intense, pulsed beams of light, for a range of different technological applications.
Krupa, Katarzyna, Tonello, Alessandro, Barthélémy, Alain, Mansuryan, Tigran, Couderc, Vincent, Millot, Guy, Grelu, Philippe, Modotto, Daniele, Babin, Sergey A., Wabnitz, Stefan (2019). Multimode nonlinear fiber optics, a spatiotemporal avenue. APL PHOTONICS, vol. 4, p. 1-44, ISSN: 2378-0967, https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.5119434
